Unveiling the Wonders of the Human Body: 100 Crucial Questions Answered (Part 1)
Introduction: The human body is a fascinating and intricate creation, comprised of numerous organs and systems that work in harmony to sustain life. In this article, we embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of the human body by providing concise answers to 100 essential questions. From the largest organ to the functions of various glands, bones, and organs, we will explore the remarkable intricacies that make up our bodies.
1. What is the largest organ in the human body?
The largest organ in the human body is the skin. It serves as a protective barrier, regulates body temperature, and aids in sensory perception.
2. Which bone protects the brain?
The bone that protects the brain is the skull or cranium, which encases and shields this vital organ.
3. How many chambers are there in the human heart?
The human heart consists of four chambers: two atria (singular: atrium) and two ventricles. The atria receive blood, while the ventricles pump blood to the rest of the body.
4. What is the function of the diaphragm?
The diaphragm is a muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity. It plays a crucial role in respiration by contracting and relaxing, allowing inhalation and exhalation.
5. Which organ is responsible for filtering waste products from the blood?
The kidneys are responsible for filtering waste products, excess water, and toxins from the blood, producing urine as a result. They also help maintain electrolyte balance and regulate blood pressure.

6. Where is the femur bone located?
The femur bone, the largest and strongest bone in the body, is located in the thigh, extending from the hip to the knee joint.
7. Which part of the digestive system is responsible for absorbing nutrients?
The small intestine is primarily responsible for absorbing nutrients from partially digested food. Its inner lining has specialized structures called villi that increase the surface area for nutrient absorption.
8. What is the main function of red blood cells?
Red blood cells, or erythrocytes, transport oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues and carry carbon dioxide, a waste product, back to the lungs for removal.
9. Where is the thyroid gland located?
The thyroid gland is located in the neck, just below the Adam’s apple. It regulates metabolism, growth, and development by producing thyroid hormones.
10. What is the purpose of the respiratory system?
The respiratory system facilitates the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the body and the environment. It includes organs such as the lungs, trachea, and bronchi.
11. Which bone is commonly known as the collarbone?
The bone commonly known as the collarbone is called the clavicle. It connects the shoulder blade (scapula) to the breastbone (sternum).
12. What is the function of the kidneys?
The kidneys perform several essential functions, including filtering waste products from the blood, maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance, producing hormones, and regulating blood pressure.
13. Where is the pancreas located in the body?
The pancreas is located behind the stomach, deep within the abdomen. It plays a vital role in digestion and blood sugar regulation by producing digestive enzymes and hormones like insulin and glucagon.
14. What is the purpose of the lymphatic system?
The lymphatic system maintains fluid balance, absorbs fats from the digestive system, removes waste products, and helps fight infections by producing and transporting white blood cells.
15. Which organ stores bile in the human body?
The gallbladder stores bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver. It releases bile into the small intestine to aid in the digestion and absorption of fats.
16. What is the role of platelets in blood clotting?
Platelets, or thrombocytes, are crucial for blood clotting. They gather at the site of an injury and form a plug to prevent excessive bleeding.
17. Where is the pituitary gland located?
The pituitary gland, often referred to as the “master gland,” is located at the base of the brain, behind the bridge of the nose. It secretes hormones that control various bodily functions and regulate other endocrine glands.
18. What is the function of the small intestine?
The small intestine is responsible for further digestion and absorption of nutrients from partially digested food received from the stomach. It plays a vital role in nutrient absorption.
19. Which bone is commonly known as the shinbone?
The bone commonly known as the shinbone is called the tibia. It is located in the lower leg and plays a crucial role in weight-bearing and movement.
20. What is the function of white blood cells in the immune system?
White blood cells, or leukocytes, play a vital role in the immune system by defending the body against infections, foreign substances, and abnormal cells. They are essential for maintaining overall health.
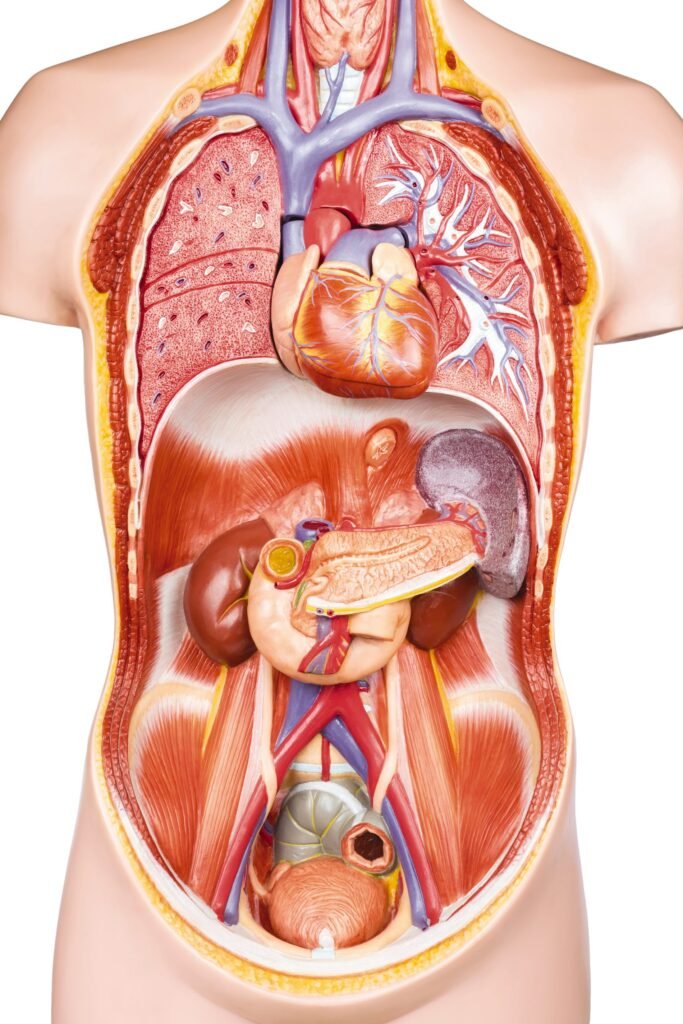
21. Where is the gallbladder located?
The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located beneath the liver, on the right side of the abdomen. It stores and concentrates bile produced by the liver.
22. What is the purpose of the urinary bladder?
The urinary bladder is a muscular sac located in the pelvis. Its main function is to store urine produced by the kidneys until it is released from the body during urination.
23. Which organ is responsible for producing insulin?
The pancreas is responsible for producing insulin. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels and allows cells to utilize glucose for energy.
24. What is the function of the cerebellum in the brain?
The cerebellum is located at the back of the brain and plays a vital role in coordinating voluntary muscle movements, maintaining balance, and posture.
25. Where is the spleen located in the body?
The spleen is located in the upper left side of the abdomen, behind the stomach. It is involved in filtering and purifying the blood, removing old or damaged red blood cells, and helping to fight infections.
26. What is the purpose of the esophagus in the digestive system?
The esophagus is a muscular tube that connects the throat (pharynx) to the stomach. Its main function is to transport food from the mouth to the stomach through a process called peristalsis.
27. Which bone is commonly known as the thigh bone?
The bone commonly known as the thigh bone is called the femur. It is the longest and strongest bone in the human body and is located in the upper leg.
28. What is the function of the adrenal glands?
The adrenal glands are located on top of each kidney. They produce hormones that regulate various bodily functions, including metabolism, stress response, blood pressure, and electrolyte balance.
29. Where is the appendix located in the body?
The appendix is a small, finger-like pouch attached to the cecum, which is the first part of the large intestine. It is located in the lower right side of the abdomen.
30. What is the purpose of the bronchi in the respiratory system?
The bronchi are the main air passages that branch off from the trachea and lead to the lungs. They transport air in and out of the lungs, allowing for gas exchange.
31. Which bone is commonly known as the kneecap?
The bone commonly known as the kneecap is called the patella. It is a small, flat, triangular bone located in front of the knee joint and protects the knee.
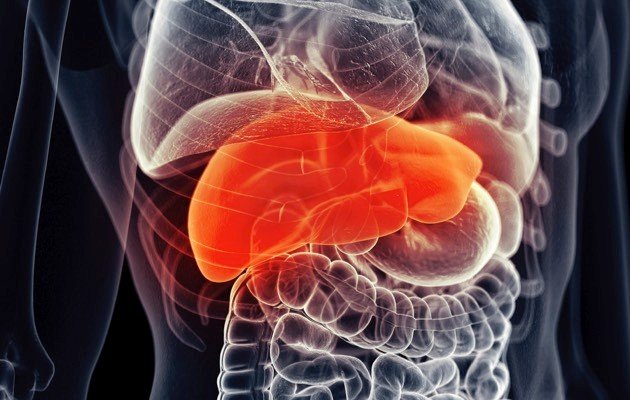
32. What is the function of the liver?
The liver is a large, complex organ located in the upper right side of the abdomen. It performs numerous essential functions, including filtering blood, detoxifying harmful substances, producing bile, storing nutrients, and metabolizing drugs and hormones.
33. Where is the thymus gland located?
The thymus gland is located in the upper chest, behind the breastbone (sternum). It plays a crucial role in the development and maturation of certain white blood cells called T-lymphocytes, which are essential for immune function.
34. What is the purpose of the large intestine in the digestive system?
The large intestine, also known as the colon, is responsible for absorbing water and electrolytes from undigested food material, forming and storing feces, and eliminating waste from the body through bowel movements.
35. Which organ is responsible for producing insulin?
The pancreas is responsible for producing insulin. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels and allows cells to utilize glucose for energy.
36. What is the function of the cerebellum in the brain?
The cerebellum is located at the back of the brain and plays a vital role in coordinating voluntary muscle movements, maintaining balance, and posture.

37. Where is the spleen located in the body?
The spleen is located in the upper left side of the abdomen, behind the stomach. It is involved in filtering and purifying the blood, removing old or damaged red blood cells, and helping to fight infections.
38. What is the purpose of the esophagus in the digestive system?
The esophagus is a muscular tube that connects the throat (pharynx) to the stomach. Its main function is to transport food from the mouth to the stomach through a process called peristalsis.
39. Which bone is commonly known as the thigh bone?
The bone commonly known as the thigh bone is called the femur. It is the longest and strongest bone in the human body and is located in the upper leg.

40. What is the function of the adrenal glands?
The adrenal glands are located on top of each kidney. They produce hormones that regulate various bodily functions, including metabolism, stress response, blood pressure, and electrolyte balance.
41. Where is the appendix located in the body?
The appendix is a small, finger-like pouch attached to the cecum, which is the first part of the large intestine. It is located in the lower right side of the abdomen.
42. What is the purpose of the bronchi in the respiratory system?
The bronchi are the main air passages that branch off from the trachea and lead to the lungs. They transport air in and out of the lungs, allowing for gas exchange.
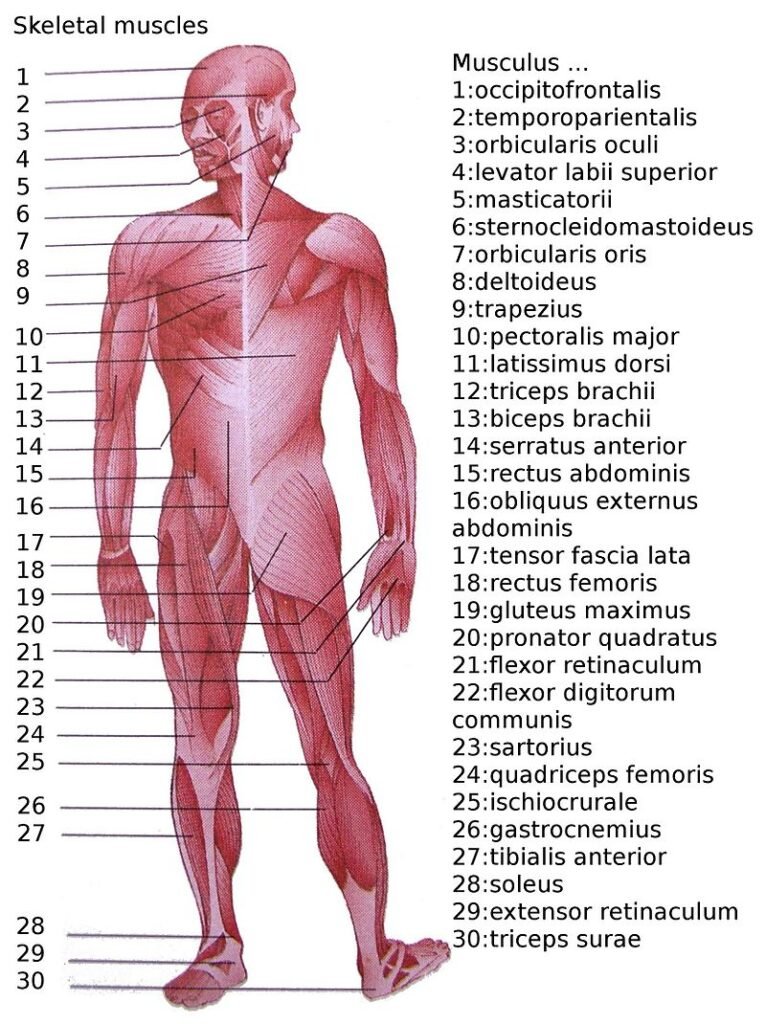
43. Which bone is commonly known as the kneecap?
The bone commonly known as the kneecap is called the patella. It is a small, flat, triangular bone located in front of the knee joint and protects the knee.
44. What is the function of the liver?
The liver is a large, complex organ located in the upper right side of the abdomen. It performs numerous essential functions, including filtering blood, detoxifying harmful substances, producing bile, storing nutrients, and metabolizing drugs and hormones.
45. Where is the thymus gland located?
The thymus gland is located in the upper chest, behind the breastbone (sternum). It plays a crucial role in the development and maturation of certain white blood cells called T-lymphocytes, which are essential for immune function.
46. What is the purpose of the large intestine in the digestive system?
The large intestine, also known as the colon, is responsible for absorbing water and electrolytes from undigested food material, forming and storing feces, and eliminating waste from the body through bowel movements.
47. Which organ produces bile to aid in digestion?
The liver produces bile, a greenish-yellow fluid that aids in the digestion and absorption of fats. Bile is stored and concentrated in the gallbladder before being released into the small intestine.
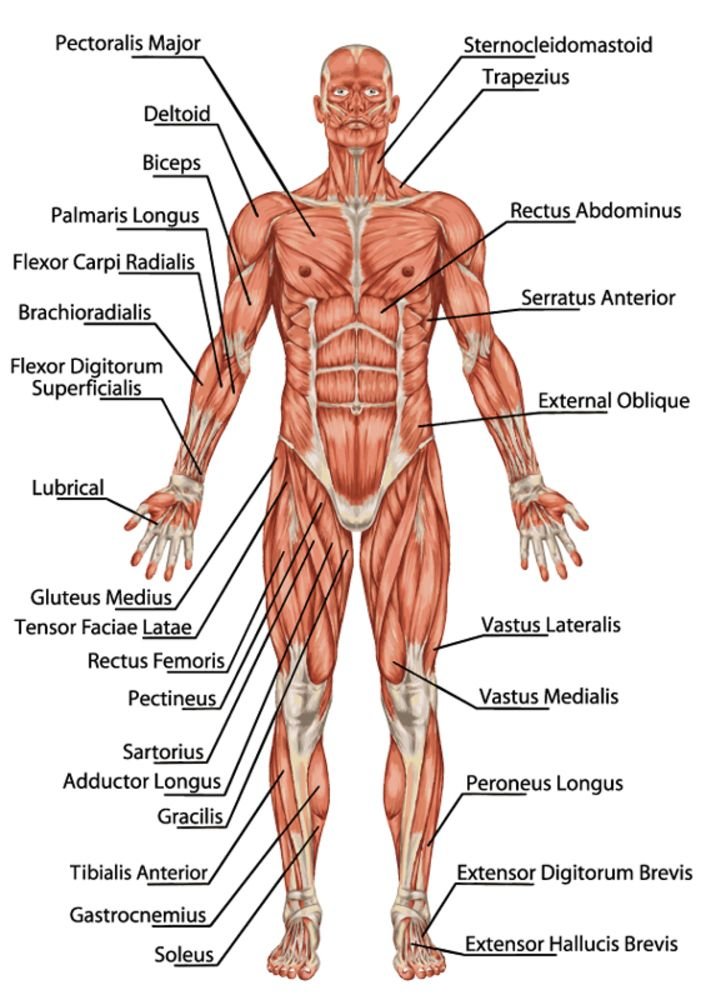
48. What is the function of the hypothalamus in the brain?
The hypothalamus is a small region located at the base of the brain. It plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including temperature, hunger, thirst, sleep, and hormone production.
49. Where is the urinary bladder located in the body?
The urinary bladder is a muscular sac located in the pelvis. Its main function is to store urine produced by the kidneys until it is released from the body during urination.
50. What is the purpose of the trachea in the respiratory system?
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a tube-like structure that connects the larynx (voice box) to the bronchi. It serves as a passageway for air to enter and exit the lungs during breathing.
Conclusions:
Unveiling the Wonders of the Human Body: 100 Crucial Questions Answered
The human body is a remarkable and intricate system that functions harmoniously to sustain life. In this article, we have delved into the depths of our physiological makeup to provide answers to 100 crucial questions about the human body. From the largest organ to the smallest bone, from the intricate functions of the brain to the complexities of the reproductive system, we have explored the wonders that lie within us.
One of the key takeaways from this exploration is the sheer complexity and interconnectedness of our bodily systems. We have discovered that the skin, the largest organ, serves as a protective barrier and regulates body temperature. We have learned that the skull, specifically the cranium, shields and safeguards the brain, the command center of our entire being.
The heart, with its four chambers, pumps life-sustaining blood throughout the body, while the diaphragm aids in the process of respiration. The kidneys filter waste products, and the liver stores bile. The pancreas produces insulin, while the thyroid gland regulates metabolism. The lymphatic system defends against infections, and the gallbladder stores bile for digestion.
From head to toe, we have explored the skeletal system, uncovering bones such as the femur, collarbone, shinbone, and kneecap. We have learned about the role of platelets in blood clotting and the functions of red and white blood cells in the circulatory and immune systems, respectively.
Furthermore, we have ventured into the realm of the endocrine system, discovering glands such as the pituitary gland, adrenal glands, and thyroid gland, which produce essential hormones for bodily functions. We have explored the digestive system, identifying organs like the small intestine, large intestine, stomach, and pancreas, each with its unique role in nutrient absorption and waste elimination.
In the realm of reproduction, we have unveiled the organs responsible for the continuation of life, such as the ovaries in females and the testes in males. We have discussed the purpose of the uterus, cervix, prostate gland, and mammary glands, all intricately involved in the processes of fertilization, pregnancy, and breastfeeding.
The brain, with its various structures like the cerebellum, hypothalamus, and hippocampus, governs our thoughts, emotions, and bodily functions. The respiratory system, with the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles, enables the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Throughout this journey, we have marveled at the complexity and interplay of these bodily systems. It is a testament to the wonders of nature and the intricate design of the human body.
By understanding the answers to these crucial questions, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and beauty of our own physical existence. It serves as a reminder of the importance of taking care of our bodies, nurturing them with proper nutrition, exercise, and self-care.
As we conclude this exploration of the human body, let us remember to marvel at the wonders within us, to treat our bodies with respect and kindness, and to continue the pursuit of knowledge and understanding of this magnificent vessel that carries us through life.
Read More:
- Comprehensive Guide: The Role of Nurses in Various Healthcare Scenarios (Part 5)
- Comprehensive Nursing Care: Addressing Diverse Patient Needs (Part 4)
- A Comprehensive Guide to Nursing Care: From Patient Documentation to Ethical Responsibilities- 20 Questions & Answers (Part 3)
- Comprehensive Insights into the Role of Nurses in Patient Care (Part 2)
- The Role of a Nurse in Healthcare: Providing Compassionate and Essential Care (Part 1)
- https://www.britannica.com/science/human-body
(To be continued for next part of this article: Unveiling the Wonders of the Human Body: 100 Crucial Questions Answered Part 2…!)