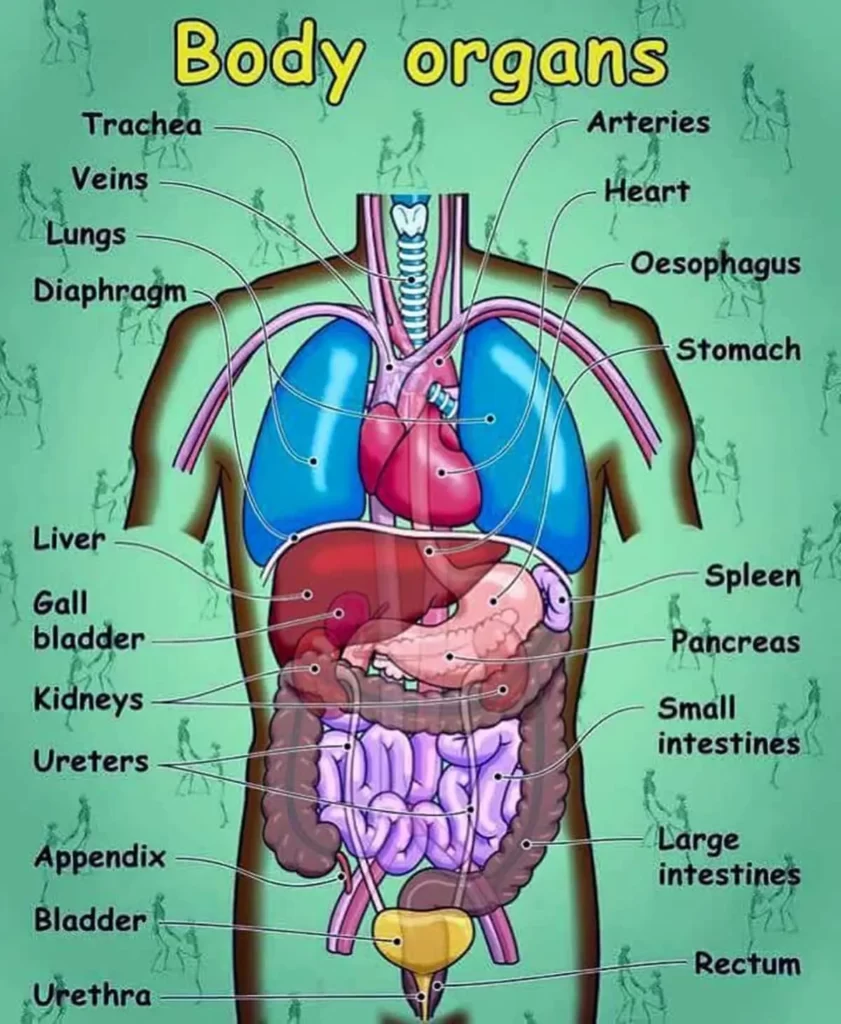
The Fascinating World of Human Physiology: Exploring the Intricacies of the Human Body (Part 2)
Introduction: Human physiology is a captivating field that delves into the intricate workings of the human body. From the production of blood cells to the perception of sensory stimuli, the human body operates through a complex network of organs, tissues, and systems. In this article, we will explore a wide range of topics in human physiology, providing answers to 100 intriguing questions (Part 2) that cover various aspects of the body’s structure and functions. Let’s embark on a journey of discovery as we uncover the secrets of hematopoiesis, sensory perception, reproductive processes, and much more.
51. Explain the process of hematopoiesis and the role of bone marrow in blood cell production.
Hematopoiesis and the Role of Bone Marrow: Hematopoiesis is the process of blood cell production, and the bone marrow plays a crucial role in this process. We will discuss the intricate steps involved in the formation of various blood cells and the significance of bone marrow as the primary site of hematopoiesis.
52. Describe the structure and functions of the spleen and its involvement in the immune system.
The Spleen and Its Involvement in the Immune System: The spleen is a vital organ involved in the immune system’s function. We will explore the structure and functions of the spleen and its contributions to the body’s defense against pathogens.
53. What are the different types of sensory receptors in the skin, and what stimuli do they respond to?
Sensory Receptors in the Skin: The skin is home to a diverse array of sensory receptors that allow us to perceive different stimuli. We will delve into the various types of sensory receptors found in the skin and their specific roles in detecting touch, temperature, and pain.
54. Explain the structure and functions of the retina and its role in vision.
The Retina and Its Role in Vision: Vision is a complex process that involves the intricate structure of the retina. We will unravel the layers of the retina, the functions of its specialized cells, and how they contribute to our ability to see.
55. Describe the structure and functions of the cochlea and its role in hearing.
The Cochlea and Its Role in Hearing: Hearing is a remarkable sensory function facilitated by the structures within the ear, particularly the cochlea. We will explore the anatomy of the cochlea and how it enables us to perceive sound.
56. What are the different types of papillae on the tongue, and what are their functions?
Papillae on the Tongue and Their Functions: The tongue plays a pivotal role in taste perception, and its surface is adorned with different types of papillae. We will uncover the various papillae on the tongue and their contributions to our sense of taste.
57. Explain the structure and functions of the spinal cord and its role in relaying nerve impulses.
The Spinal Cord and Nerve Impulse Transmission: The spinal cord is an essential component of the central nervous system and acts as a conduit for transmitting nerve impulses. We will discuss the structure of the spinal cord and its role in relaying sensory and motor signals.
58. Describe the structure and functions of the autonomic nervous system.
The Autonomic Nervous System: The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary bodily functions, maintaining homeostasis. We will delve into the structure and functions of this system, exploring its sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions.
59. What are the major hormones produced by the adrenal glands, and what are their functions?
Hormones Produced by the Adrenal Glands: The adrenal glands produce vital hormones that play a role in various physiological processes. We will identify the major hormones secreted by the adrenal glands and their functions in the body.
60. Explain the process of spermatogenesis and the role of the testes in male reproduction.
Spermatogenesis and the Role of the Testes: Spermatogenesis is the process of sperm cell production, primarily occurring in the testes. We will discuss the intricacies of spermatogenesis and the essential functions of the testes in male reproduction.
61. Describe the structure and functions of the epidermal layers of the skin.
The Epidermal Layers of the Skin: The skin’s outermost layer, the epidermis, serves as a protective barrier. We will explore the different layers of the epidermis and their roles in maintaining skin health.
62. What are the major lymph nodes located in the body, and what are their roles in the immune system?
Lymph Nodes and Their Roles in the Immune System: Lymph nodes are integral to the immune system’s function, acting as hubs for immune cell activity. We will elucidate the major lymph nodes in the body and their contributions to immune responses.
63. Explain the process of light refraction and how it contributes to vision.
Light Refraction and Vision: The process of light refraction is crucial for vision, enabling us to focus and perceive objects clearly. We will examine how light is refracted by the eye’s structures and its significance in visual perception.
64. Describe the structure and functions of the semicircular canals and their role in balance.
The Semicircular Canals and Balance: Balance is a complex function facilitated by the semicircular canals within the ear. We will explore the structure of these canals and their role in maintaining equilibrium.
65. What are the different types of olfactory receptors in the nose, and how do they detect smells?
Olfactory Receptors in the Nose: Our sense of smell relies on olfactory receptors within the nasal cavity. We will delve into the different types of olfactory receptors and their ability to detect various smells.
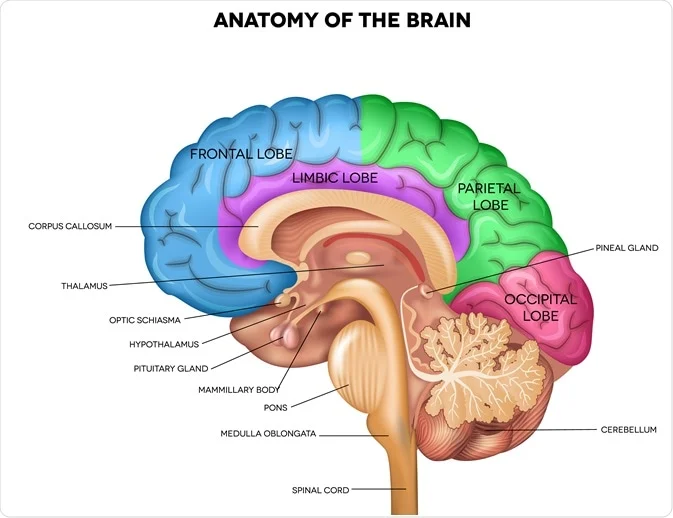
66. Explain the structure and functions of the cerebrum and its role in higher cognitive functions.
The Cerebrum and Higher Cognitive Functions: The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and is responsible for higher cognitive functions. We will discuss the structure of the cerebrum and its role in memory, language, and decision-making.
67. Describe the structure and functions of the peripheral nerves and their role in transmitting signals.
Peripheral Nerves and Signal Transmission: The peripheral nerves extend throughout the body, transmitting signals between the central nervous system and peripheral tissues. We will examine the structure of peripheral nerves and their role in conveying sensory and motor information.

68. What are the major hormones produced by the thyroid gland, and what are their functions?
Hormones Produced by the Thyroid Gland: The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism, growth, and development. We will identify the major hormones secreted by the thyroid gland and their functions in the body.
69. Explain the process of oogenesis and the role of the ovaries in female reproduction.
Oogenesis and the Role of the Ovaries: Oogenesis is the process of egg cell development, which occurs within the ovaries. We will explore the intricate stages of oogenesis and the essential functions of the ovaries in female reproduction.
70. Describe the structure and functions of the dermal layers of the skin.
The Dermal Layers of the Skin: Beneath the epidermis lies the dermis, a layer rich in blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue. We will discuss the structure and functions of the dermis, including its contributions to skin elasticity and sensation.
71. What are the major lymphatic vessels in the body, and how do they transport lymph?
The Major Lymphatic Vessels: Lymphatic vessels play a crucial role in transporting lymph, a fluid vital for immune system function. We will identify the major lymphatic vessels in the body and how they facilitate the movement of lymph.
72. Explain the process of sound transmission and how it is perceived by the auditory system.
Sound Transmission and Auditory Perception: Sound transmission is a complex process that involves the ear’s structures and auditory pathways. We will explore how sound waves are transmitted, converted into neural signals, and perceived as sound.
73. Describe the structure and functions of the taste buds on the tongue and their role in taste perception.
Taste Buds on the Tongue and Taste Perception: Taste buds are responsible for our ability to discern different flavors. We will delve into the structure of taste buds, the types of taste receptors they contain, and how they contribute to taste perception.
74. What are the major components of the reflex arc, and how do they contribute to reflex actions?
Reflex Arc and Reflex Actions: Reflex actions are rapid, involuntary responses to stimuli that help protect the body from harm. We will discuss the components of the reflex arc and their contributions to reflex actions.
75. Explain the structure and functions of the cerebellum and its role in motor coordination.
The Cerebellum and Motor Coordination: The cerebellum plays a crucial role in coordinating motor movements, balance, and posture. We will explore the structure and functions of the cerebellum and its involvement in motor control.
76. Describe the structure and functions of the cranial nerves and their respective functions.
The Cranial Nerves and Their Functions: The cranial nerves emerge directly from the brain and serve various sensory and motor functions. We will identify the twelve cranial nerves and discuss their respective roles.
77. What are the major hormones produced by the pituitary gland, and what are their functions?
Hormones Produced by the Pituitary Gland: The pituitary gland, often referred to as the “master gland,” secretes hormones that regulate numerous bodily functions. We will elucidate the major hormones produced by the pituitary gland and their functions.
78. Explain the process of fertilization and implantation in the female reproductive system.
Fertilization and Implantation in the Female Reproductive System: Fertilization is the union of sperm and egg cells, leading to the formation of a zygote. We will explain the intricate process of fertilization and subsequent implantation in the female reproductive system.

79. Describe the structure and functions of the subcutaneous layer of the skin.
The Subcutaneous Layer of the Skin: The subcutaneous layer, also known as the hypodermis, is the deepest layer of the skin. We will examine the structure and functions of the subcutaneous layer, including its role in insulation and energy storage.
80. What are the major lymphoid tissues, and how do they contribute to the immune response?
Lymphoid Tissues and the Immune Response: Lymphoid tissues are essential for immune cell development and activation. We will explore the major lymphoid tissues, such as the lymph nodes, spleen, and thymus, and their contributions to the immune response.

81. Explain the process of color vision and the role of different photoreceptor cells.
Color Vision and Photoreceptor Cells: Color vision relies on specialized photoreceptor cells in the retina. We will explain how different types of photoreceptor cells enable us to perceive colors and distinguish between different wavelengths of light.
82. Describe the structure and functions of the utricle and saccule and their role in balance.
The Utricle and Saccule in Balance: The utricle and saccule are structures within the vestibular system that contribute to balance and orientation. We will discuss their anatomy and their role in detecting linear acceleration and gravity.
83. What are the different types of receptors involved in tactile sensation, and where are they located?
Receptors for Tactile Sensation: Tactile sensation allows us to perceive touch, pressure, and vibration. We will explore the different types of receptors involved in tactile sensation and where they are located in the skin.

84. Explain the structure and functions of the brainstem and its role in vital functions.
The Brainstem and Vital Reflexes: The brainstem is responsible for essential functions such as breathing, heart rate regulation, and swallowing. We will examine the structure of the brainstem and its role in coordinating vital reflexes.
85. Describe the structure and functions of the peripheral nervous system subdivisions (somatic and autonomic).
The Peripheral Nervous System Subdivisions: The peripheral nervous system comprises the somatic and autonomic subdivisions. We will delve into the structure and functions of these subdivisions and their respective roles in voluntary and involuntary bodily functions.
86. What are the major hormones produced by the pancreas, and what are their functions?
Hormones Produced by the Pancreas: The pancreas produces important hormones involved in glucose regulation and digestion. We will identify the major hormones secreted by the pancreas and their functions in the body.
87. Explain the process of menstrual cycle regulation and hormonal feedback mechanisms.
Menstrual Cycle Regulation and Hormonal Feedback Mechanisms: The menstrual cycle is regulated by intricate hormonal feedback mechanisms. We will explain the process of menstrual cycle regulation and the role of hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, and luteinizing hormone.

88. Describe the structure and functions of the hypodermis layer of the skin.
The Hypodermis Layer of the Skin: The hypodermis, also known as the subcutaneous layer, serves important functions in insulation and protection. We will explore the structure and contributions of the hypodermis to overall skin health.
89. What are the major lymphatic organs, and what are their roles in immune function?
Lymphatic Organs and Immune Function: Lymphatic organs play key roles in immune cell development, maturation, and immune responses. We will describe the major lymphatic organs, including the thymus, bone marrow, and spleen, and their contributions to immune function.
90. Explain the process of depth perception and the role of binocular vision.
Depth Perception and Binocular Vision: Depth perception allows us to perceive the relative distances of objects in our surroundings. We will discuss the process of depth perception and the crucial role of binocular vision in perceiving depth.
91. Describe the structure and functions of the ampullae and utricles in the vestibular system.
The Ampullae and Utricles in the Vestibular System: The ampullae and utricles are important structures within the vestibular system, contributing to our sense of balance and spatial orientation. We will explore their structure and functions in detail.
92. What are the different types of cutaneous receptors, and what stimuli do they respond to?
Cutaneous Receptors and Stimuli Detection: The skin contains various types of cutaneous receptors that detect different types of stimuli. We will examine the different types of cutaneous receptors and the stimuli they respond to, such as pressure, temperature, and pain.
93. Explain the structure and functions of the medulla oblongata and its role in vital reflexes.
The Medulla Oblongata and Vital Reflexes: The medulla oblongata, located in the brainstem, plays a crucial role in coordinating vital reflexes such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure regulation. We will discuss its structure and functions.
94. Describe the structure and functions of the spinal nerves and their distribution.
The Endocrine System and Hormone Signaling: The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete hormones, regulating various bodily functions. We will explore the endocrine system’s structure, hormone signaling pathways, and its coordination with the nervous system.
95. What are the major hormones produced by the gonads, and what are their functions?
Hormones Produced by the Gonads: The gonads, including the testes in males and the ovaries in females, produce important hormones involved in reproduction and sexual development. We will identify the major hormones produced by the gonads and their functions.
96. Explain the process of fertilization and embryonic development after implantation.
The Placenta and Its Role in Pregnancy: The placenta is a temporary organ that develops during pregnancy, providing essential functions for fetal development and maternal-fetal communication. We will explain the structure and functions of the placenta.
97. Describe the structure and functions of the submucosa layer of the skin.
The Arrector Pili Muscles and Hair Follicles: Arrector pili muscles are tiny muscles attached to hair follicles, causing hair to stand up when stimulated. We will explore the anatomy of hair follicles and the role of arrector pili muscles.
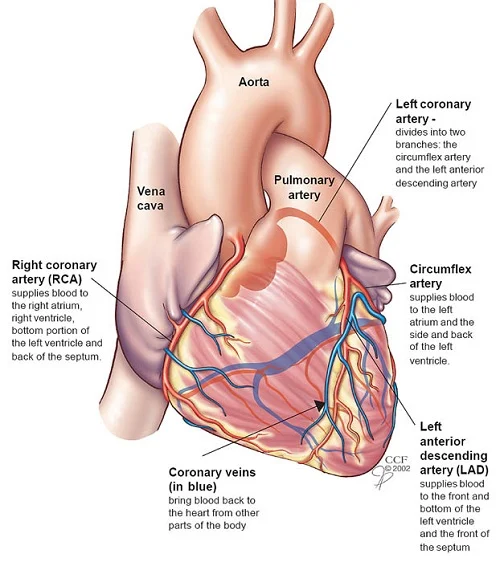
98. What are the primary lymphoid organs, and what is their role in immune cell development?
Lymphatic Circulation and Immune Cell Transport: Lymphatic circulation is responsible for transporting lymph and immune cells throughout the body. We will discuss the pathways of lymphatic circulation and how immune cells are transported.
99. Explain the process of auditory perception and the role of the auditory cortex.
Chemoreceptors and Chemical Sensation: Chemoreceptors are specialized sensory receptors that detect chemical stimuli, such as taste and smell. We will delve into the different types of chemoreceptors and their contributions to chemical sensation.
100. Describe the structure and functions of the Meissner’s and Pacinian corpuscles and their role in touch sensation.
Thermoreceptors and Temperature Sensation: Thermoreceptors are sensory receptors that detect changes in temperature. We will explore the different types of thermoreceptors and their role in temperature sensation and regulation.
Conclusion:
Human physiology is a vast and fascinating field that encompasses a multitude of processes and mechanisms within the human body. In this article, we have explored a wide range of topics, providing answers to 100 intriguing questions ( Part 2) about the intricacies of human physiology. From the production of blood cells to the perception of sensory stimuli, each aspect of the human body’s structure and function is remarkable and essential for our existence. By unraveling these mysteries, we gain a deeper understanding of ourselves and the intricate workings that make us who we are.
https://www.britannica.com/science/human-body
- 50 Questions And Answers-Anatomy and Physiology: Exploring the Human Body’s Structure and Functions
- Unveiling the Wonders of the Human Body: 100 Crucial Questions Answered (Part 2)
- Unveiling the Wonders of the Human Body: 100 Crucial Questions Answered (Part 1)
- Understanding the Human Body: 20 Essential Questions Answered
- Comprehensive Guide: The Role of Nurses in Various Healthcare Scenarios (Part 5)

