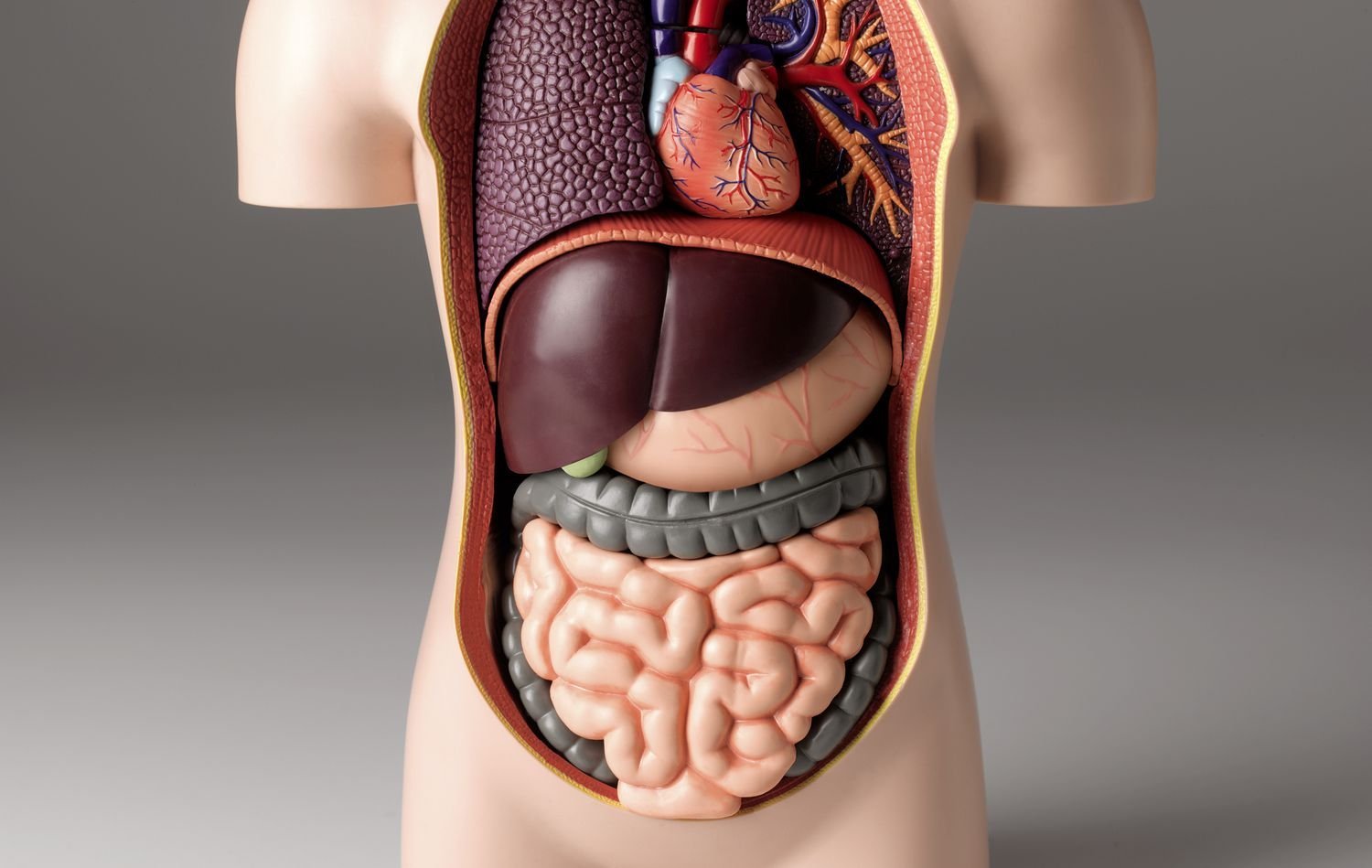
Understanding the Human Body: 20 Essential Questions Answered
Introduction: The human body is a marvel of complexity and precision, with various organs and systems working together seamlessly to sustain life. Understanding the functions and structures of these components is crucial to comprehending our own bodies. In this article, we will provide concise answers to 20 fundamental questions about the human body, shedding light on its remarkable design and functionality.
1. What is the largest organ in the human body?
The largest organ in the human body is the skin. It serves as a protective barrier, regulating body temperature, and plays a vital role in sensory perception.
2. Which bone protects the brain?
The bone that protects the brain is called the skull or cranium. It provides a sturdy enclosure that shields the delicate brain from potential injuries.
3. How many chambers are there in the human heart?
The human heart consists of four chambers: two atria (singular: atrium) and two ventricles. The atria receive blood, while the ventricles pump blood to the rest of the body.
4. What is the function of the diaphragm?
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle located beneath the lungs. Its primary function is to facilitate respiration by contracting and relaxing, causing inhalation and exhalation.
5. Which organ is responsible for filtering waste products from the blood?
The kidneys are responsible for filtering waste products, excess water, and toxins from the blood, producing urine as a result. They also help maintain electrolyte balance and regulate blood pressure.
6. Where is the femur bone located?
The femur bone is the longest and strongest bone in the human body. It is located in the thigh, extending from the hip to the knee joint.
7. Which part of the digestive system is responsible for absorbing nutrients?
The small intestine is the part of the digestive system primarily responsible for absorbing nutrients from food. It has a large surface area lined with specialized structures called villi, which enhance nutrient absorption.
8. What is the main function of red blood cells?
Red blood cells, or erythrocytes, carry oxygen from the lungs to all parts of the body and transport carbon dioxide, a waste product, back to the lungs for removal.
9. Where is the thyroid gland located?
The thyroid gland is situated in the neck, just below the Adam’s apple. It plays a vital role in regulating metabolism, growth, and development.
10. What is the purpose of the respiratory system?
The respiratory system is responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the body and the environment. It includes organs such as the lungs, trachea, and bronchi.
11. Which bone is commonly known as the collarbone?
The bone commonly known as the collarbone is called the clavicle. It connects the shoulder blade (scapula) to the breastbone (sternum).
12. What is the function of the kidneys?
The kidneys perform several essential functions, including filtering waste products from the blood, maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance, producing hormones, and regulating blood pressure.
13. Where is the pancreas located in the body?
The pancreas is located behind the stomach, deep within the abdomen. It produces digestive enzymes and hormones, such as insulin and glucagon, that regulate blood sugar levels.
14. What is the purpose of the lymphatic system?
The lymphatic system is responsible for maintaining fluid balance, removing waste and toxins from tissues, and supporting immune function by producing and transporting white blood cells.
15. Which organ stores bile in the human body?
The gallbladder stores bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver. It releases bile into the small intestine to aid in the digestion and absorption of fats.
16. What is the role of platelets in blood clotting?
Platelets are small, disc-shaped blood cells that play a crucial role in blood clotting or coagulation. They clump together to form a plug at the site of injury, preventing excessive bleeding.
17. Where is the pituitary gland located?
The pituitary gland is a pea-sized gland located at the base of the brain, within a bony cavity called the sella turcica. It produces and releases hormones that regulate various bodily functions.
18. What is the function of the small intestine?
The small intestine is responsible for further digestion and absorption of nutrients from partially digested food received from the stomach. It is a vital organ for nutrient absorption.
19. Which bone is commonly known as the shinbone?
The bone commonly known as the shinbone is called the tibia. It is located in the lower leg, connecting the knee to the ankle, and plays a crucial role in weight-bearing and movement.
20. What is the function of white blood cells in the immune system?
White blood cells, or leukocytes, are key components of the immune system. They help defend the body against infections, foreign substances, and abnormal cells, playing a vital role in maintaining overall health.
Conclusion:
Understanding the human body’s intricate mechanisms and structures is essential for appreciating its complexity and ensuring its well-being. By addressing these 20 fundamental questions, we have gained insights into some of the most significant aspects of human anatomy and physiology. The human body is a remarkable masterpiece of nature, and exploring its mysteries continues to be an intriguing journey of discovery.
https://www.britannica.com/list/13-questions-about-how-the-human-body-works-answered
- Comprehensive Guide: The Role of Nurses in Various Healthcare Scenarios (Part 5)
- Comprehensive Nursing Care: Addressing Diverse Patient Needs (Part 4)
- A Comprehensive Guide to Nursing Care: From Patient Documentation to Ethical Responsibilities- 20 Questions & Answers (Part 3)
- Comprehensive Insights into the Role of Nurses in Patient Care (Part 2)
- The Role of a Nurse in Healthcare: Providing Compassionate and Essential Care (Part 1)